Let’s explain in simple terms what’s the U.S. insurance system.
In life, there may be various adverse situations where you may need to incur large expenses.
But they may or may not happen.
To protect oneself from them, the insurance contract has been invented: you pay a certain premium, and then, when an insured event (illness, car damage, disability) occurs, the company pays you the sum insured to cover the expenses. In Russia this system is still in its infancy, in America, it has been established long ago.
Part of an American’s paycheck goes to insurance, which is a mandatory budget item.
So, in the U.S. we can distinguish the following types of insurance:
- medical;
- social;
- pension;
- real estate;
- life;
- deposits;
- auto insurance.
Now for more details about each type.
Medical in U.S. Insurance System.
in the United States, there is no free health care; it has been completely replaced by a system of paid health insurance. Let’s try to explain all the main nuances.
Under the Affordable Care Act (or Obamacare), the major health insurance law of the United States, it is the responsibility of every U.S. citizen to buy insurance.
If for some reason he does not have insurance, he may even be fined.
Who pays for insurance?
Your property and social status are important – it will depend on it who will have to pay the amount of insurance. The following options are possible:
- If you are low-income, disabled, or unemployed, the state pays for coverage (Medicaid);
- If your income is low and your employer does not pay for insurance, you have the responsibility, but the state pays part of the cost;
- The most common situation is that all or part of the cost is borne by the employer if you are employed and have at least an average income;
- If you work in the U.S. and have a steady income, but your employer does not pay for insurance, these costs are again on you. This may be due to the nature of the job.
- And finally, the last case: when you turn 65, the insurance is paid by the state under a special Medicare program.
Where and when the policy is issued?
You can buy insurance on special Internet resources: some states use a federal site, and some states have their own sites.
It is there that you can read in detail about the main conditions of insurance plans offered by different organizations and choose the appropriate one for yourself.
Under Obamacare, you can buy insurance from November 15 to February 15 every year. Previously, by the way, there was no such time limit.
What are the types of health insurance?
Now let’s look at the main types of health insurance. All of them can be divided into the following varieties:
- Health Maintenance Organization (HMO). As a rule, the most inexpensive insurances. You choose a general practitioner, who will supervise you in the future (something like district doctors in Russia). It is this doctor who has the right to refer you to more specific specialists. However, you will not be able to get medical care everywhere, only in certain organizations. By the way, it is interesting to know how much a doctor earns under this system of work. Information here. Compare with the current situation of doctors in Russia.
- Exclusive Provider Organization (EPO). Generally similar to the previous type, but in this case, there is no attachment to a therapist: you visit doctors on your own. The limits of care are similar to those of the HMO.
- Preferred Provider Organization (PPO). This is the more expensive type of insurance, and if you have it, you get the most favorable health insurance terms. So, you can get care not only from the “basic organizations”, but from almost any medical organization (though usually, this comes with a surcharge). You don’t have to work with a general practitioner: You can see the specialist you want at the medical facility of your choice on your own.
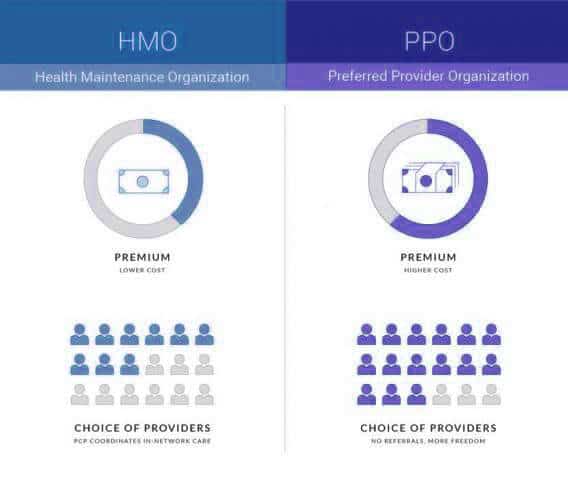
When you buy one of these types of insurance, you agree to pay the premiums specified in the contract each month. In the U.S., the premium is called a premium. It is usually $200 to $500 per person.
On the one hand, it may seem rather expensive, but sometimes the cost of operations comes to $20,000-30,000, so it is still worth paying those premiums.
Insurance coverage
Another important point about insurance: sometimes it doesn’t cover the entire cost of treatment.
This is why we need to distinguish several terms, which we will focus on in more detail.
Co-pay is a co-pay for medical services. For example, you visit a doctor, pay a co-pay of $30, and the insurance company covers the rest.
Deductible – A cap on the amount you pay for medical services. The bottom line: when your medical expenses reach a certain amount, the insurance company will cover them in larger amounts later under Co-insurance (more about that below).
Co-insurance is a percentage payment for health care by you and the insurance company.
For example, the ratio could be as follows: 15 percent goes to you and 85 percent to the insurance company. Recall that this system arises after your expenses exceed the deductible.
There is another important term within the U.S. MHI system: Out-of-pocket maximum. This is also a cap, just like the Deductible, but once your medical expenses have reached this amount, the insurance firm pays the full cost of all subsequent medical services for you.
Once the insurance year passes, everything is reset, and you proceed again in the same pattern from the beginning.
Social Security
In addition to medical care, the United States has a well-developed social insurance system. Here the insured cases are as follows: unemployment, disability, loss of a breadwinner, old age (we will consider the issue of pensions separately).
If health insurance is non-public, then here the contributions are paid to the budgets (federal and the budget of the respective state where you live).

How the system is organized?
Let’s first look at how the U.S. social security system is generally organized. Every working citizen has an important document, the Social Security Number (SSN), which certifies that you are eligible for Social Security. It also serves as your Social Security Number card.
The number of benefits in the event of an insured event will be calculated depending on how long you have worked, what your income was, etc. You should, however, distinguish it from social security, which is not tied to insurance; it is paid by the state to the poor, orphans, and others in need (for example, certain categories are given free school lunches, housing, etc.).
What are the specifics of obtaining one of the major U.S. documents? What can you count on when you have a Social Security Number? Answers to these and other questions are in the following video.
What are the Types of Social Insurance?
Loss of breadwinner
It is paid if the deceased person was insured, was working, and the family has lost their main source of income, thus needing additional financial support. This benefit is paid to family members of the deceased (usually the spouse). If the deceased has left dependents, the amount of the welfare payment increases.
On temporary disability
Persons who have worked and become disabled (invalids) due to an illness that is not work-related can qualify for it.
General conditions: five years of work and a fixed number of premiums paid (as a rule, the employer pays them for the employee) are required.
From unemployment
The contribution amount is 6.2 percent of annual income, but there are numerous nuances associated with state participation in adjusting this number. As a general rule, are paid by employers.
The payment of these contributions helps guarantee the insured in the event of unemployment the payment of appropriate benefits. The latter amount to an average of $250 to $300.
From occupational injuries (occupational diseases).
If a temporary disability allowance is paid when the illness is not work-related, the situation here is exactly the opposite (the payments, in this case, will also be higher). The employer pays the contributions.
Pension System
Every U.S. citizen is insured against old age, and if an insured event occurs (the general rule is to reach the age of 65), he or she can claim a pension.
Let’s look at the main points about the U.S. public pension program, as well as the nuances of private pension insurance.
Accrual of Pensions
The U.S. Social Security Administration is responsible for calculating pensions, and it is this agency that assigns citizens the Social Security number already mentioned.
Working citizens pay a so-called pension tax, which amounts to 7.65% of income if total annual income does not exceed $65,000. 6.2% goes toward paying toward a future pension, and 1.45% goes toward medical care. Interestingly, if your income is above $65,000, only 1.45% is charged.
Note: this amount is paid by the employee himself. At the same time, the employer must pay exactly the same contribution, which means that the pension savings are actually 15% of income.
As a rule, the retirement age is 65, but for people with disabilities, it can be less – 62 years.
True, in the latter case, three years not worked will affect the amount of pension, which will be slightly lower.
If the insurance experience (that is, the period when pension contributions were paid) is less than 10 years, the pension is not paid at all, and the citizen is left with the only way out – to apply for a poverty allowance.
Savings pension
In addition, a U.S. citizen can transfer a portion of the pension insurance contribution to a funded fund to form a funded pension in the future.
After 5-7 years, a person who makes contributions to the funded fund will be able to access these funds.
Quite a number of Americans receive a funded pension as a supplement to their basic pension. There are both public and private funded funds.
Personal Retirement Account
In addition to the basic state pension and the funded pension, a citizen has the opportunity to open an individual retirement account (personal pension account). Here he/she can transfer sums of money, which are not tied to taxes or insurance contributions.
The annual threshold for money that can be contributed is $2,000.
At age 60 you can withdraw this money, but once a retiree reaches age 80 this account will be closed.
Many people are not as interested in the pension system as in the actual retirement benefits paid to American citizens.
The average pension in the United States is 1300-1400 dollars, which is one of the highest in the world.
And this is despite the fact that this does not take into account people’s savings formed in a savings fund.
We recommend looking at it. In America, it is customary to think about your pension long before you retire.
It’s not uncommon to turn to a financial advisor to calculate savings.
Life Insurance
Most Americans not only participate in social and health insurance but also take out life insurance. Unlike the previous types, they are insured on a case-by-case basis, which means that there is no single system.
If a person wishes to insure his life, so that in case of death his family members get a solid insurance payout, he chooses a suitable company on the market and concludes a contract with it.
Life insurance terms are determined by the agreement between the company and the citizen.
Premiums can be paid either during a certain period or as a lump sum.




